Halma
| Overview |
 Halma (meaning "jump" in Greek) is a two-player abstract board game invented in 1883 (or 1884) by George Howard Monks. Halma (meaning "jump" in Greek) is a two-player abstract board game invented in 1883 (or 1884) by George Howard Monks.
|
| Board |
|
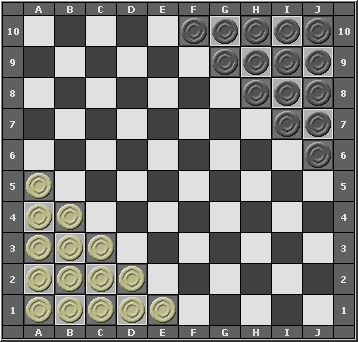
The original Halma is played on a 16x16 checkerboard but other sizes can be used too. igGameCenter uses a 10x10 checkerboard. Each player has 15 checkers (dark and light) located in opposite corners of the board. The areas where the checkers are placed are called "houses".
|
| Objective |
| The goal of the Halma is to move all of your own checkers from your own house to the opponent's house. |
| Play |
|
Players move alternately one checker per turn, starting with the player with the light checkers. There are two variants of moving a checker:
|
| End of Game |
|
When a player makes a move that results in all his checkers being located in the opponent's house the player wins. One exception is made to this rule for balancing the game. Since the player with light checkers has the advantage of the first move the dark player gets one extra turn after the light player moves all his checkers to the dark house. If the dark player succeeds in moving all his checkers into the light house using the extra turn then the game ends in a draw. |
Game statistics

Game activity graph

TOP20 list of members by the score

TOP20 list of members by the number of wins

TOP20 list of members by the number of played games